Mechanism of action
While the majority of antioxidants are simply based on a supply of exogenous molecules, which are quickly depleted, Melorun® does much more: it stimulates the endogenous defences because the most important antioxidants are not what we eat, but what our bodies produce.

Oxidative stress, a matter of balance
As a result of normal metabolism, the body produces free radicals, even at rest. Involved in cellular communication and the immune response, these unstable and highly reactive molecules are best known for their role in oxidative stress.
During exercise, the increase in metabolism may be associated with an increased production of these radicals. The oxidative stress and inflammation induced are likely to cause many negative effects that can impact performance and recovery.
To counteract this process, our body depends on molecules capable of slowing down or even preventing oxidation: these are antioxidants.
Why are not all antioxidants the same?
(1) The balance between beneficial effects and damage induced by free radicals is particularly fragile. To stabilise the balance, the body can rely on both an internal defence system and external sources of antioxidants.
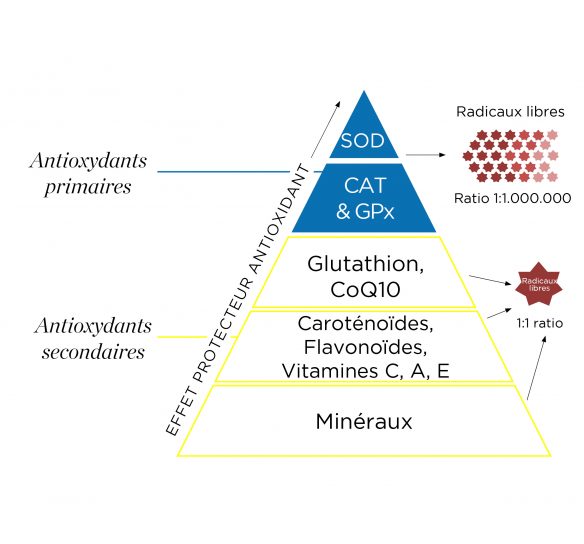
(2) The first molecules involved in this fight, primary antioxidants, are enzymes naturally produced by the body.
Three primary antioxidant enzymes, Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Catalase (CAT) and Glutathione peroxidase (GPx), control the first stages of oxidative stress and keep the anti-/pro-oxidant balance in equilibrium, even before its initiation.
Capable of catalysing millions of reactions without becoming depleted, they provide continuous and lasting antioxidant protection.
(3) Exclusively provided by food, secondary antioxidants (vitamins, minerals, polyphenols, etc.) act much later. They give up electrons to unstable free radicals and neutralise them, but run out quickly, without the possibility of renewal.
Melorun®, an original and proven mode of action
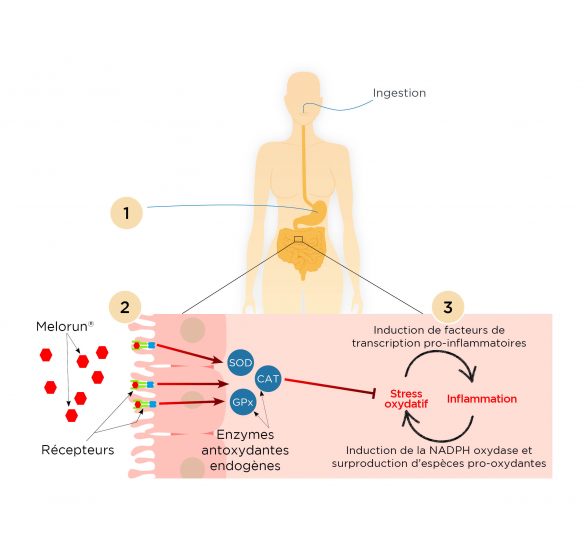
(1)After absorption, our patented coatings protect Melorun® from acid attack, allowing it to be released into the gastrointestinal tract without being denatured. However, even if our ingredient manages to reach the intestine unscathed, a major limitation remains: SOD is too large a molecule to be able to cross the intestinal barrier and pass into the blood. And yet, many studies have reported the beneficial effects of Melorun® supplementation.
(2)Our studies have shown that by interacting with receptors in the intestinal wall, Melorun® induces a reaction cascade resulting in the expression of the three primary antioxidant enzymes: SOD, CAT and GPX.
(3)Without being absorbed, Melorun® stimulates the body’s antioxidant defences and maintains a beneficial level of free radicals.